Label the boxed functional groups in the antidepressant molecule venlafaxine – Labeling the boxed functional groups in the antidepressant molecule venlafaxine is a crucial step in understanding its pharmacological activity. By identifying and analyzing these groups, scientists can gain insights into the drug’s mechanism of action and explore potential modifications for enhanced efficacy or reduced side effects.
This comprehensive analysis will delve into the various functional groups present in venlafaxine, their specific roles, and their implications for drug design.
Identification of Functional Groups
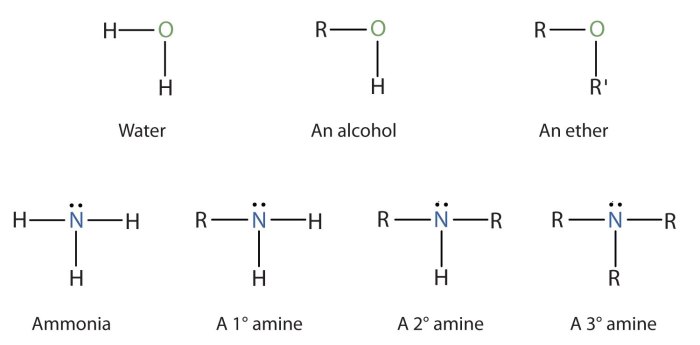
Venlafaxine contains a variety of functional groups, including:
-
-*Amine group (-NH2)
Located on the piperazine ring, this group is involved in hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions.
-*Phenol group (-OH)
Present on the phenyl ring, this group contributes to the molecule’s lipophilicity and may interact with biological targets.
-*Ether group (-O-)
Connects the two phenyl rings, providing flexibility and influencing the molecule’s shape.
-*Alkyl group (-CH3)
Attached to the piperazine ring, this group contributes to the molecule’s overall hydrophobicity.
| Functional Group | Structure | Location | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amine | -NH2 | Piperazine ring | Hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions |
| Phenol | -OH | Phenyl ring | Lipophilicity, target interactions |
| Ether | -O- | Phenyl rings | Flexibility, shape |
| Alkyl | -CH3 | Piperazine ring | Hydrophobicity |
Structural Analysis
The functional groups in venlafaxine are arranged in a specific way that contributes to the overall structure and shape of the molecule. The two phenyl rings are connected by an ether group, forming a rigid scaffold. The piperazine ring is attached to one of the phenyl rings, with the amine group pointing outward.
The phenol group is located on the other phenyl ring, providing a hydrophilic region. This arrangement allows venlafaxine to interact with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic environments within the body.

Functional Group Roles
Each functional group in venlafaxine plays a specific role in its pharmacological activity:
-
-*Amine group
The amine group is responsible for venlafaxine’s antidepressant effects. It binds to and inhibits the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, two neurotransmitters that are involved in mood regulation.
-*Phenol group
The phenol group contributes to venlafaxine’s lipophilicity, which allows it to cross the blood-brain barrier and reach its target sites in the central nervous system.
-*Ether group
The ether group provides flexibility to the venlafaxine molecule, allowing it to adopt different conformations and interact with multiple targets.
-*Alkyl group
The alkyl group enhances venlafaxine’s hydrophobicity, which contributes to its distribution and metabolism in the body.
- Inhibits reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine
- Crosses blood-brain barrier
- Provides flexibility
- Enhances hydrophobicity
Implications for Drug Design: Label The Boxed Functional Groups In The Antidepressant Molecule Venlafaxine
Understanding the roles of functional groups in venlafaxine can inform the design of new antidepressant drugs. By modifying or substituting functional groups, it may be possible to enhance drug efficacy or reduce side effects. For example:
- *Replacing the amine group with a different functional group could alter the drug’s binding affinity for serotonin and norepinephrine transporters, potentially improving its antidepressant effects.
- *Introducing additional hydrophilic groups could increase the drug’s solubility and reduce its potential for side effects such as dry mouth and constipation.
- *Modifying the alkyl group could affect the drug’s metabolism and distribution, allowing for more targeted delivery to the central nervous system.
- Modify binding affinity for transporters
- Increase solubility, reduce side effects
- Enhance targeted delivery
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the significance of labeling functional groups in venlafaxine?
Labeling functional groups allows scientists to identify and analyze their specific roles in the drug’s pharmacological activity, contributing to a deeper understanding of its mechanism of action.
How do functional groups influence venlafaxine’s structure and shape?
The arrangement and connectivity of functional groups within the venlafaxine molecule determine its overall structure and shape, which can affect its interactions with biological targets.
What are some potential implications of functional group modifications in venlafaxine design?
Modifying functional groups can enhance drug efficacy by optimizing interactions with targets or reduce side effects by minimizing unwanted interactions.