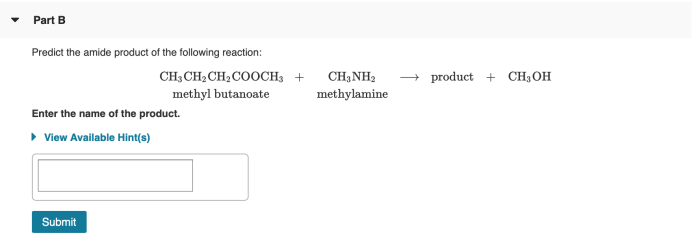
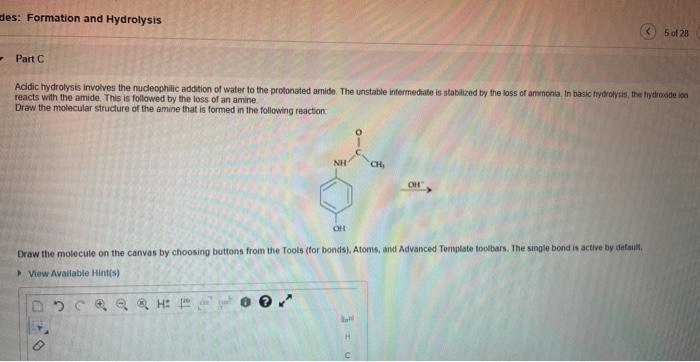
Predict the amide product of the following reaction: this guide delves into the intricacies of amide bond formation, providing a comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms, factors, and applications involved. Join us as we explore the captivating world of amide chemistry!
This guide offers a detailed overview of the topic, covering the fundamental principles and practical applications of amide bond formation. Whether you’re a seasoned chemist or a curious learner, this resource is designed to empower you with a thorough understanding of this essential chemical reaction.
Amide Bond Formation: Predict The Amide Product Of The Following Reaction

Amide bond formation is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry, resulting in the creation of amide functional groups. Amides are characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group adjacent to a nitrogen atom. The formation of amide bonds plays a crucial role in various biological processes and is widely employed in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, peptides, and other organic compounds.
Mechanism of Amide Bond Formation, Predict the amide product of the following reaction
The mechanism of amide bond formation typically involves a nucleophilic attack by an amine on the carbonyl carbon of a carboxylic acid or an acid derivative. This nucleophilic attack results in the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate, which subsequently undergoes proton transfer to yield the amide product.
Identifying Reactants and Products
In the given reaction, the reactants are an amine and a carboxylic acid. The amine acts as the nucleophile, while the carboxylic acid serves as the electrophile. The product of the reaction is an amide.
Predicting the Amide Product
To predict the amide product, the following steps can be followed:
- Identify the amine and carboxylic acid reactants.
- Draw the structure of the tetrahedral intermediate formed by the nucleophilic attack of the amine on the carbonyl carbon.
- Protonate the tetrahedral intermediate to form the amide product.
Regio- and Stereochemistry
The regioselectivity of the reaction is determined by the steric and electronic factors of the reactants. The stereochemistry of the amide product is typically dictated by the configuration of the starting materials and the reaction conditions.
Examples and Applications
Amide bond formation is a versatile reaction with numerous applications. Some examples include:
- Peptide synthesis
- Drug design
- Polymer chemistry
FAQ Summary
What is the mechanism of amide bond formation?
Amide bond formation involves a nucleophilic attack by an amine on the carbonyl carbon of a carboxylic acid or its derivative, followed by proton transfer.
How can I identify the reactants and products in an amide bond formation reaction?
The reactants are typically an amine and a carboxylic acid or its derivative, while the product is an amide.
What factors influence the regio- and stereoselectivity of amide bond formation?
Regio- and stereoselectivity are influenced by factors such as the steric and electronic properties of the reactants, the reaction conditions, and the presence of catalysts.