A referendum is not purely direct democracy because the – A referendum is not purely direct democracy because it involves the delegation of decision-making power to elected representatives. While referendums allow citizens to vote on specific issues, the ultimate authority to make binding decisions rests with the elected officials. This distinction highlights the complex interplay between direct and representative democracy, raising questions about the true nature of democratic governance.
Referendums, while providing a mechanism for citizen participation, are limited in their ability to fully represent the will of the people. Factors such as voter turnout, campaign dynamics, and media influence can skew the outcomes of referendums, potentially leading to decisions that do not reflect the broader public sentiment.
1. Definition of Direct Democracy
Direct democracy is a form of government in which citizens have the power to make decisions directly, without the intermediary of elected representatives. This means that citizens vote directly on laws, policies, and other matters that affect their lives.
2. Referendum as a Form of Direct Democracy
A referendum is a vote in which citizens are asked to approve or reject a specific proposal or policy. Referendums can be used to make decisions on a wide range of issues, from local matters to national constitutional amendments.
3. Limitations of Referendums
- Referendums can be expensive and time-consuming to hold.
- Referendums can be misleading, as voters may not have all the information they need to make an informed decision.
- Referendums can be divisive, as they can pit different groups of citizens against each other.
4. Role of Elected Representatives
In a representative democracy, citizens elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf. These representatives are accountable to the people who elected them and can be voted out of office if they do not represent their constituents’ interests.
5. Comparison of Referendums and Representative Democracy

- Referendums:Direct democracy, citizens vote directly on laws and policies.
- Representative democracy:Indirect democracy, citizens elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf.
6. Factors Influencing Referendum Outcomes

- Public opinion
- Media coverage
- Campaign strategies
7. Historical Examples of Referendums: A Referendum Is Not Purely Direct Democracy Because The
The Swiss referendum system is one of the oldest and most extensive in the world. Swiss citizens have voted on a wide range of issues, from the adoption of a new constitution to the construction of a new nuclear power plant.
8. Current Trends in Referendum Use
There has been a growing trend towards the use of referendums in recent years. This is due in part to the rise of populism and the decline of trust in traditional political institutions.
9. Future of Referendums
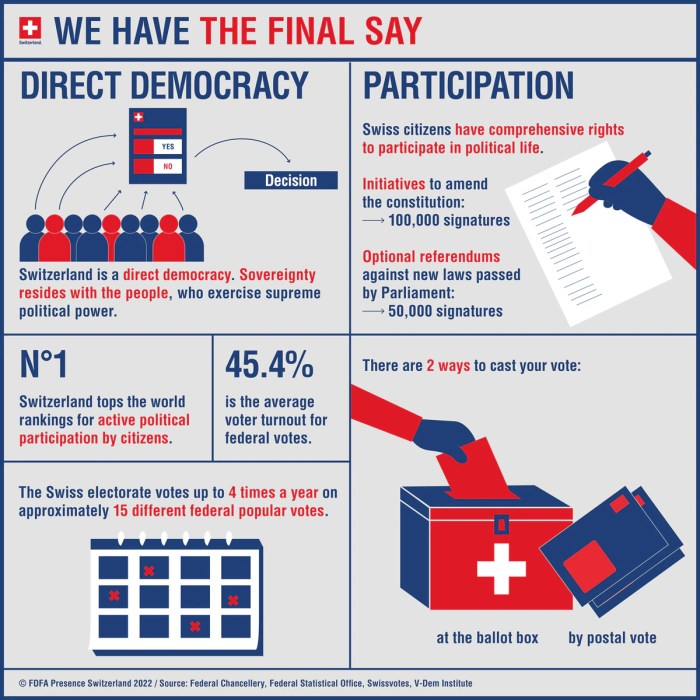
The future of referendums is uncertain. Some experts believe that referendums will become more common as citizens become more engaged in the political process. Others believe that referendums will become less common as representative democracy becomes more responsive to the needs of the people.
Q&A
What is the key difference between a referendum and direct democracy?
In direct democracy, citizens directly make binding decisions on public matters, while in a referendum, citizens vote on specific issues, but the final decision-making authority rests with elected representatives.
Why are referendums not always considered a true form of direct democracy?
Referendums may not fully represent the will of the people due to factors such as low voter turnout, campaign dynamics, and media influence, which can skew the outcomes.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of referendums?
Advantages include increased citizen participation and the ability to address specific issues. Disadvantages include the potential for outcomes that do not reflect broader public sentiment and the delegation of decision-making power to elected representatives.