What is the x component fx of the resultant force – What is the x component (Fx) of the resultant force? It’s a fundamental concept in physics that measures the force acting along the x-axis. Understanding Fx is crucial for analyzing forces in various fields, including engineering, mechanics, and everyday life.
This comprehensive guide delves into the definition, factors affecting, applications, limitations, and extensions of Fx, providing a thorough understanding of this important force component.
1. Definition of the x component fx of the resultant force
The x component fx of the resultant force is the component of the resultant force that acts along the x-axis. The resultant force is the vector sum of all the forces acting on an object. It is a measure of the net force acting on the object and is responsible for causing the object to accelerate.
The x component fx can be calculated using the following formula:
“`fx = ΣFx“`where:* ΣFx is the sum of all the forces acting on the object along the x-axis
The units of measurement for fx are newtons (N). 1 N is equal to the force required to accelerate a 1 kg object at a rate of 1 m/s^2.
2. Factors affecting the x component fx
The magnitude and direction of fx are influenced by several factors, including:
- The magnitude of the forces acting on the object:The greater the magnitude of the forces acting on the object, the greater the magnitude of fx.
- The direction of the forces acting on the object:The direction of fx is determined by the direction of the resultant force. The resultant force is the vector sum of all the forces acting on the object.
- The mass of the object:The mass of the object affects the acceleration of the object. The greater the mass of the object, the smaller the acceleration for a given force.
The following table summarizes the factors that affect fx and their effects:
| Factor | Effect on fx |
|---|---|
| Magnitude of the forces | Directly proportional |
| Direction of the forces | Determines the direction of fx |
| Mass of the object | Inversely proportional |
3. Applications of the x component fx
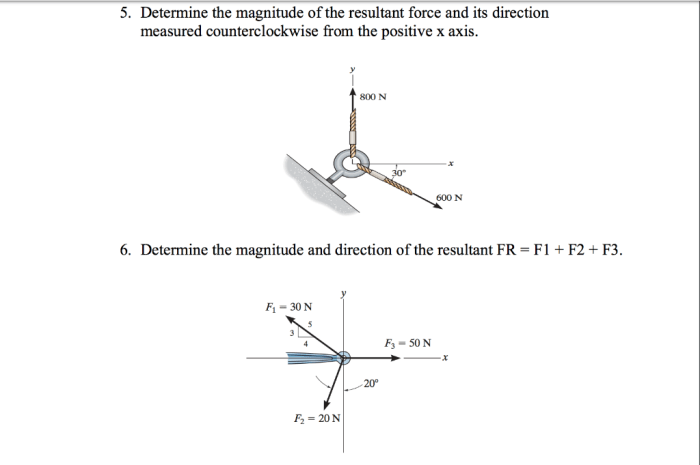
Fx is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Engineering:Fx is used to calculate the forces acting on structures, such as bridges and buildings.
- Physics:Fx is used to study the motion of objects. It is used to calculate the acceleration of an object and to determine the forces that are acting on it.
- Sports:Fx is used to analyze the forces that are involved in sports, such as running and jumping.
Understanding fx is important in a variety of fields, including engineering, physics, and sports.
4. Limitations of the x component fx: What Is The X Component Fx Of The Resultant Force

While fx is a useful measure of force, it does have some limitations. One limitation is that it only measures the force acting along the x-axis. It does not measure the force acting along the y-axis or the z-axis.
Another limitation is that fx does not take into account the point of application of the force. The point of application of the force can affect the moment of the force and the resulting motion of the object.
In some cases, it may be necessary to use a more complex measure of force, such as the vector sum of all the forces acting on an object, to accurately describe the forces acting on an object.
5. Extensions of the x component fx
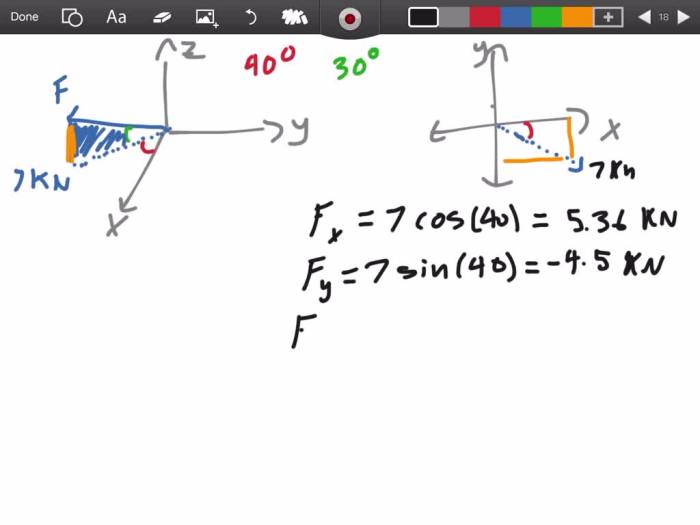
There are several extensions or variations of the concept of fx. One extension is the concept of the moment of a force. The moment of a force is a measure of the force’s ability to rotate an object about an axis.
Another extension is the concept of the center of pressure. The center of pressure is the point at which the resultant force of a fluid acting on a surface acts. The center of pressure is important in fluid mechanics and is used to calculate the forces acting on objects in fluids.
These extensions of the concept of fx enhance our understanding of force analysis and are used in a variety of applications.
Query Resolution
What is the formula for calculating Fx?
Fx = F cos(theta), where F is the magnitude of the resultant force and theta is the angle between the force and the x-axis.
What factors affect the magnitude of Fx?
The magnitude of Fx is influenced by the magnitude of the resultant force and the angle theta.
What are some applications of Fx in real-world scenarios?
Fx is used in engineering to analyze forces in structures, in mechanics to calculate the motion of objects, and in everyday life to understand the forces acting on objects.
