Figure 11-2 is an anterior view of the heart – Figure 11-2, an anterior view of the heart, provides a comprehensive visual representation of the heart’s external anatomy. This perspective offers valuable insights into the heart’s structure, blood flow patterns, and clinical significance.
The anterior view allows for the identification of key anatomical landmarks, including the atria, ventricles, major blood vessels, and valves. By examining this view, healthcare professionals can assess the heart’s size, shape, and any potential abnormalities.
Introduction: Figure 11-2 Is An Anterior View Of The Heart
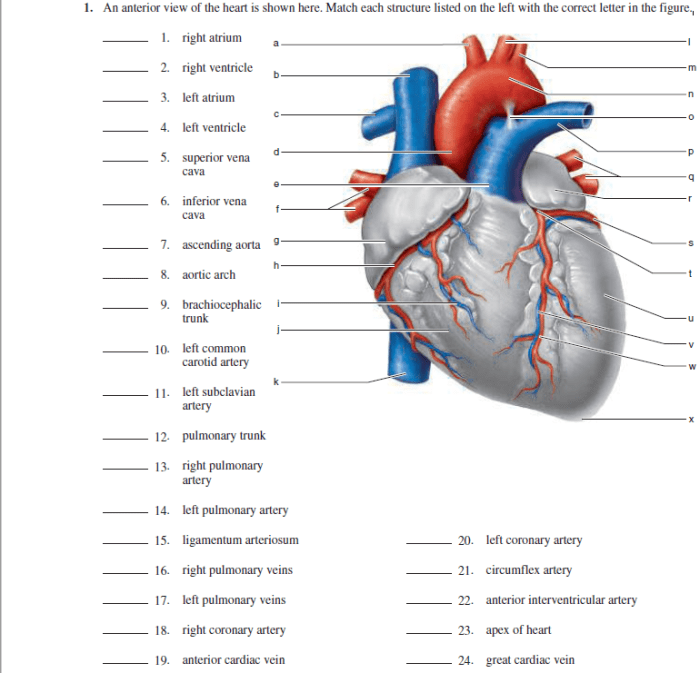
The heart is a vital organ responsible for pumping oxygenated blood throughout the body. The anterior view of the heart provides a clear visualization of its external anatomy and major blood vessels.
Figure 11-2 presents an anterior view of the heart, which allows us to analyze the arrangement and relationships of various anatomical structures.
Anatomical Structures
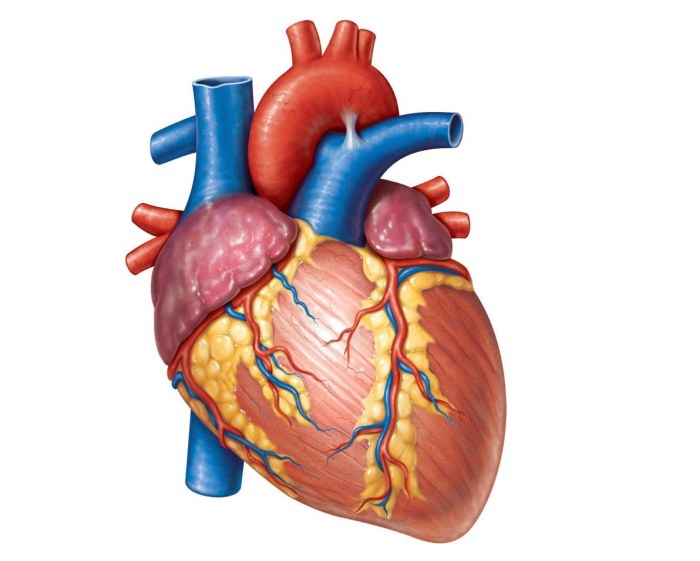
Major Anatomical Structures, Figure 11-2 is an anterior view of the heart
| Structure | Description |
|---|---|
| Right Atrium | Chamber that receives deoxygenated blood from the body. |
| Right Ventricle | Chamber that pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs. |
| Left Atrium | Chamber that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. |
| Left Ventricle | Chamber that pumps oxygenated blood to the body. |
| Aorta | Main artery that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart. |
| Pulmonary Artery | Artery that carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. |
| Pulmonary Veins | Veins that carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. |
| Superior Vena Cava | Vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the heart. |
| Inferior Vena Cava | Vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the heart. |
Blood Flow
Blood enters the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava, which deliver deoxygenated blood to the right atrium. From the right atrium, blood flows into the right ventricle, which contracts and pumps the blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
In the lungs, blood picks up oxygen and returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins, which deliver oxygenated blood to the left atrium. The blood then flows into the left ventricle, which contracts and pumps the oxygenated blood out of the heart through the aorta to the rest of the body.
Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle refers to the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart chambers, which occurs in two phases: systole and diastole.
During systole, the ventricles contract, pushing blood out of the heart. During diastole, the ventricles relax, allowing blood to fill the chambers.
The heart valves, including the tricuspid valve, pulmonary valve, mitral valve, and aortic valve, ensure the proper flow of blood through the heart and prevent backflow.
Clinical Significance
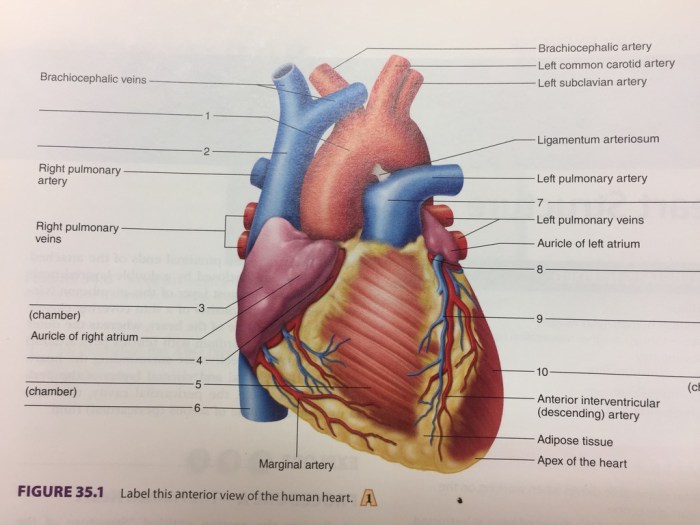
Understanding the anterior view of the heart is essential for medical professionals in various ways:
- Medical Imaging:The anterior view is commonly used in medical imaging techniques, such as echocardiography, to assess the heart’s structure and function.
- Diagnostic Procedures:The anterior view allows physicians to visualize the heart’s anatomy and identify any abnormalities, such as valve defects or blockages in blood vessels.
- Surgical Interventions:The anterior view provides guidance for surgeons during cardiac surgeries, such as valve replacements or bypass procedures.
Questions and Answers
What is the purpose of the anterior view of the heart?
The anterior view of the heart provides a comprehensive visual representation of the heart’s external anatomy, allowing for the identification of key anatomical landmarks and assessment of the heart’s size, shape, and potential abnormalities.
How is the anterior view of the heart used clinically?
The anterior view of the heart is used in medical imaging techniques, such as echocardiography, to diagnose and manage cardiovascular conditions.