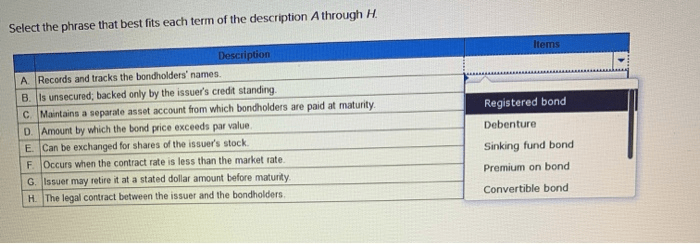
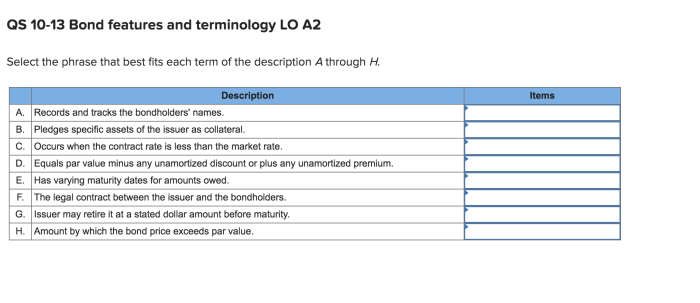
Records and tracks the bondholders names – Records and tracks the bondholders’ names are essential for maintaining accurate and up-to-date records of who owns bonds. This information is crucial for various purposes, including making interest payments, sending out notices, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
This comprehensive guide provides an overview of the methods used to identify bondholders, the different record-keeping systems available, and the processes involved in data collection, management, reporting, and disclosure. It also addresses the challenges associated with data collection and the importance of data security and privacy.
Identify Bondholders
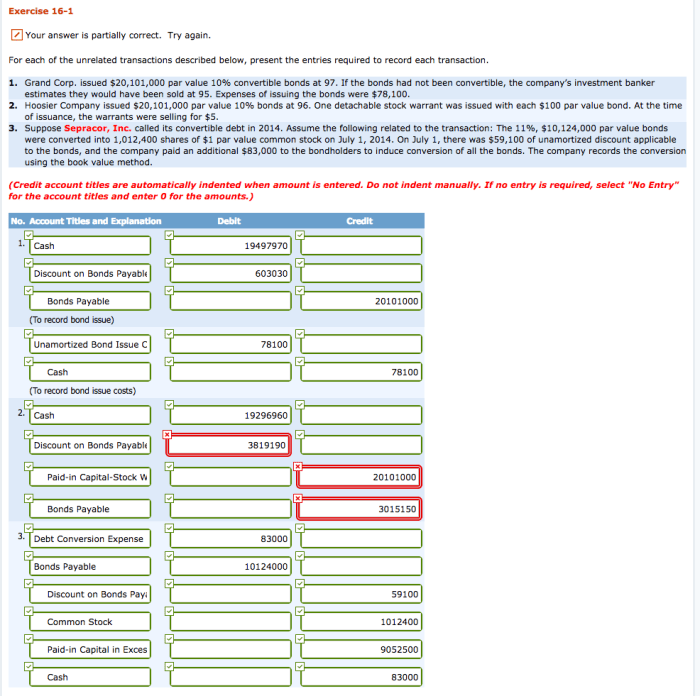
Recording and tracking bondholders’ names is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it enables the issuer to communicate effectively with bondholders, providing them with essential updates, notices, and financial information. Secondly, it helps ensure that interest payments and redemptions are made to the correct parties, minimizing the risk of errors or fraud.
Thirdly, it facilitates the transfer of bonds between bondholders, ensuring a smooth and transparent process.
To maintain accurate and up-to-date records, it is essential to implement robust identification procedures. These procedures may include:
- Obtaining legal documentation, such as certificates of beneficial ownership or trust indentures, that provide proof of bond ownership.
- Verifying bondholder information through independent sources, such as brokerage firms or custodians.
- Utilizing electronic systems that allow bondholders to register their ownership directly with the issuer.
Record-Keeping Systems
Various record-keeping systems can be employed to track bondholders’ names. Each system offers unique advantages and disadvantages:
Manual Systems, Records and tracks the bondholders names
Manual systems involve the use of physical records, such as paper ledgers or spreadsheets. While they are relatively inexpensive and easy to implement, they are prone to errors and can be cumbersome to manage, especially for large numbers of bondholders.
Electronic Systems
Electronic systems, such as databases or online portals, offer greater efficiency and accuracy. They allow for automated record-keeping, easy data retrieval, and enhanced security measures. However, they require significant investment and technical expertise to implement and maintain.
Hybrid Systems
Hybrid systems combine elements of both manual and electronic systems. They provide a balance between cost-effectiveness and efficiency, offering a scalable solution for organizations with varying record-keeping needs.
| Feature | Manual Systems | Electronic Systems | Hybrid Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low | High | Moderate |
| Accuracy | Lower | Higher | Moderate |
| Scalability | Limited | High | Moderate |
| Security | Lower | Higher | Moderate |
Data Collection
Collecting bondholders’ names can be challenging, particularly for large or widely dispersed bondholder bases. Methods used to collect data include:
- Contacting bondholders directly through mail, email, or phone to request their information.
- Obtaining data from third-party sources, such as brokerage firms or custodians, who hold bonds on behalf of their clients.
- Utilizing online platforms or portals that allow bondholders to register their ownership and provide contact information.
It is important to note that data collection efforts should adhere to privacy and data protection regulations, ensuring that bondholder information is handled securely and confidentially.
Data Management
Once bondholder data has been collected, it must be managed effectively to ensure its accuracy, security, and accessibility. Data management processes include:
- Regularly updating and verifying bondholder information to maintain its accuracy.
- Implementing robust security measures to protect bondholder data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Establishing clear data access protocols to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information.
Best practices for data management include:
- Utilizing data encryption and other security measures to protect sensitive information.
- Regularly backing up data to prevent loss in case of system failures or breaches.
- Establishing clear data retention policies to ensure that bondholder information is stored for the appropriate period.
Reporting and Disclosure
Issuers are required to report and disclose bondholder information to various stakeholders, including regulatory authorities, investors, and bondholders themselves. Reporting requirements may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the type of bond issued.
Common types of reports and disclosures include:
- Periodic financial statements that disclose the number and value of bonds outstanding, as well as the names of major bondholders.
- Bondholder lists that provide detailed information about each bondholder, including their name, address, and bond ownership details.
- Offering circulars and other offering documents that provide information about the terms of the bond issue, including the rights and obligations of bondholders.
Reporting formats may vary depending on the requirements of the relevant regulatory authority or the specific bond issue.
Detailed FAQs: Records And Tracks The Bondholders Names
What are the benefits of maintaining accurate and up-to-date records of bondholders?
Accurate records facilitate timely interest payments, ensure effective communication with bondholders, and enable compliance with regulatory reporting requirements.
What are the challenges associated with collecting bondholders’ names?
Challenges include obtaining information from multiple sources, handling name changes and address updates, and ensuring the accuracy and completeness of data.
What are the best practices for managing bondholder data?
Best practices include implementing robust data security measures, establishing clear data retention policies, and regularly reviewing and updating data to ensure accuracy.